Grid Connection Services are an essential part of the power system, connecting generation with loads. A grid connection is necessary at all levels – transmission, distribution, and industrial grid. A grid connection regulates the voltage level in the system to match the electrical demands. A grid system consists of transformers, protective devices that help protect both equipment and personnel against injuries or damages caused by high voltages or current overloads. Grid connection also consists of measuring instruments like meters which monitor supplies to consumers.
Grid Connection Types: Grid systems can be mainly divided into three types based on various parameters like Voltage levels, network type, supply features, etc. The different types are listed below:
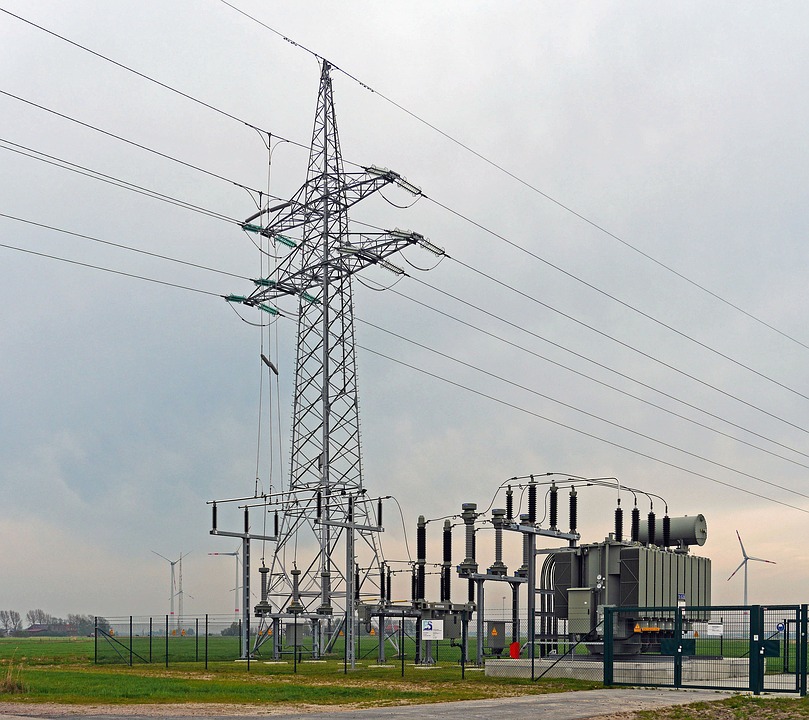
Transmission connection: The transmission system operates at a very high voltage level, well over 220kV. The transmission grid consists of specialties like power stations, transmission lines, and substations. The transmission grid is generally well planned before commencement to avoid any interference with the land-use pattern. Power flow in the network is bi-directional, which means it can be either from one side or both sides (from two different sources).
Substation level connections: This type of connection is carried out between generator and main distribution point or load point like transformer. Substations are the most important part of the power system since they act as hubs to distribute electricity through power lines to end consumers. The installation cost for substations depends on the load, distance, and number of consumers. It also depends on the voltage level, location of the substation, etc.
Distribution connection: The distribution system operates at medium or low voltage levels from 2kV to 35kv. In distribution grids, maximum power flow is in one direction towards the consumer end. This type of grid is generally radial in nature with a single source, i.e., it consists of only one line that splits into different feeders for respective areas/sectors before distributing electricity to consumers. For this reason, the installation cost for the distribution grid is relatively less when compared with transmission connection which requires more materials and expertise to install higher voltage lines in a shorter span.
Spur Lines: Spur line is an offshoot of the mainline of the transmission grid and runs only to one side (generally consumer end). Spur lines distribute electricity from a nearby station or sub-station to end-users.
Loop Line: Loop line is an offshoot of a transmission system that runs in the opposite direction, i.e., it diverts power flow from source to the source instead of consumers, as illustrated below:
Types based on connection status: Grid Connection Services can also be classified as Active and Inactive. An active connection is one that supplies electricity continuously, while inactive connections are those which were once active but no longer supplied due to some reason like load growth, generator up-gradation, etc.



Leave a Reply